Table of contents
Open Table of contents
The Enigma of Steganography: Hiding Messages in Plain Sight
In an era where information is currency, the art of concealing messages within digital files has gained paramount importance. This covert practice, known as steganography, empowers individuals to embed messages, images or even sounds within seemingly unremarkable data. Steganography’s history and practical uses are as intriguing as they are diverse.
An Age-Old Practice
The roots of steganography extend far beyond the digital age, back to ancient Greece. Clever methods of information concealment were employed to safeguard sensitive messages. One classic example involved scraping wax from tablets, writing a message on the underlying wood, and recovering them with wax. These tablets appeared blank, allowing them to pass inspection by sentries.
Tattoos and Secrets
In another ingenious method, messengers had their heads shaved and messages or images tattooed on their scalps. As their hair regrew, the message remained hidden until the next shave.
A Spy’s Deception
Even spies recognized the value of steganography. In one case, a seemingly innocent message, “Apparently neutral’s protest is thoroughly discounted and ignored. Isman hard hit. Blockade issue affects pretext for embargo on by-products, ejecting suets and vegetable oils,” concealed the real message: “Pershing sails from NY June 1.” Such methods exemplify the art of hiding in plain sight.
A Digital Frontier
In today’s digital landscape, steganography has evolved into a captivating blend of art and science. It entails the concealment of data within the vast realm of ones and zeros that constitute digital files. This technique can be applied to various forms of media, from images to audio and video, allowing hidden messages to be embedded within.
Types of Message Concealment
Steganography encompasses a variety of techniques, including watermarking, fingerprinting, and robust, and fragile methods. Watermarking is commonly used for embedding copyright information, allowing creators to claim ownership of their works. Fingerprinting, on the other hand, embeds a serial number within a cover object, aiding in the identification of the last legitimate owner or user of media.
Robust Steganography
Robust steganography aims to ensure that hidden messages remain intact, even in the face of data compression. High-quality media can preserve their watermarks, even when subjected to lossy compression. This is made possible by adding watermarks in the frequency domain, which allows them to withstand compression while retaining their integrity.
Examples of how to hide a text inside an Image:
1. Open an Image (it has to be a BMP format as it has a smaller size and it should be in greyscale) inside the winhip_en.exe Program we’ll use it to hide text inside our Image:
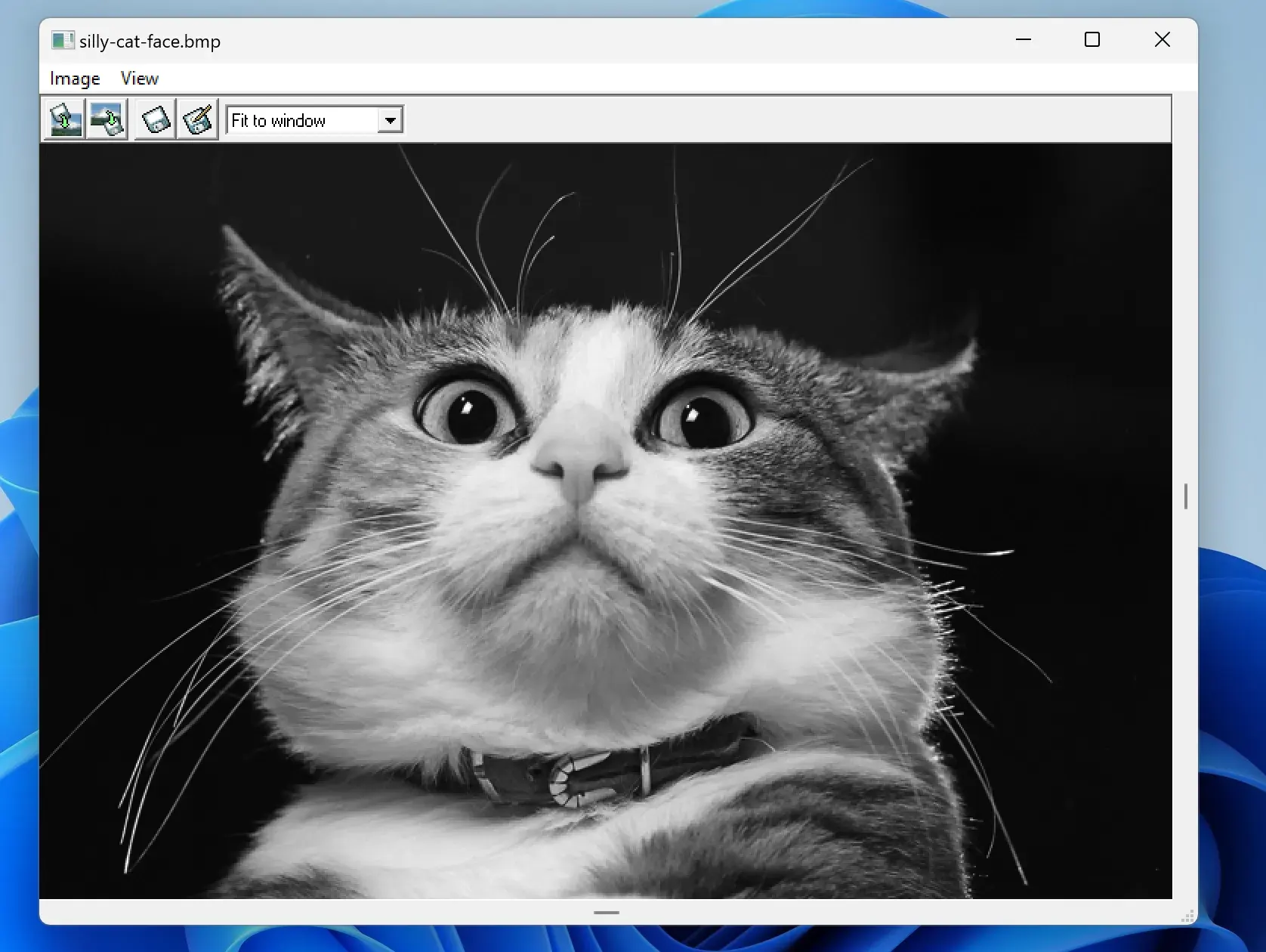
2. From the menu above go to Image => hide file then select the text file you want to hide inside the image:
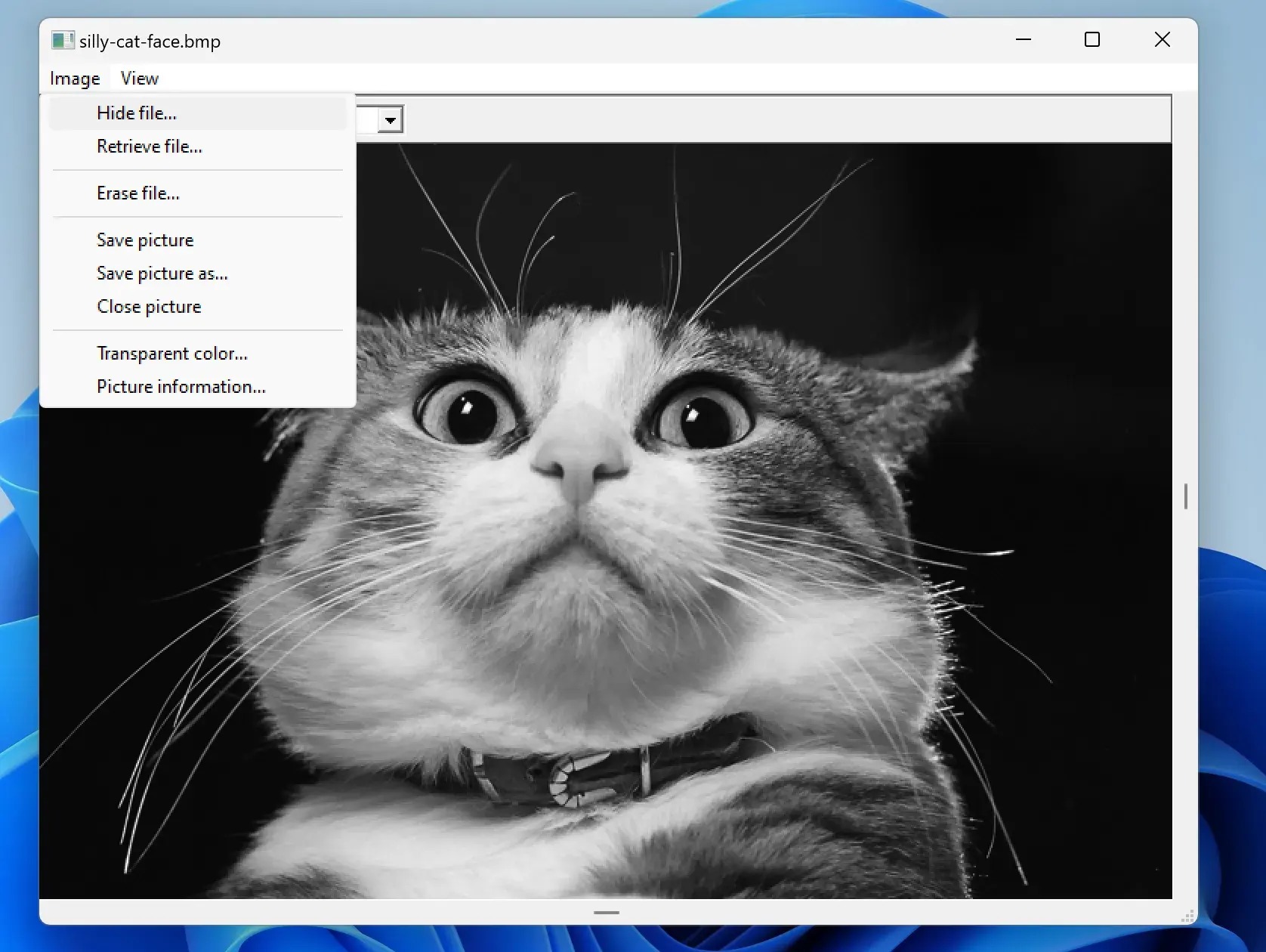
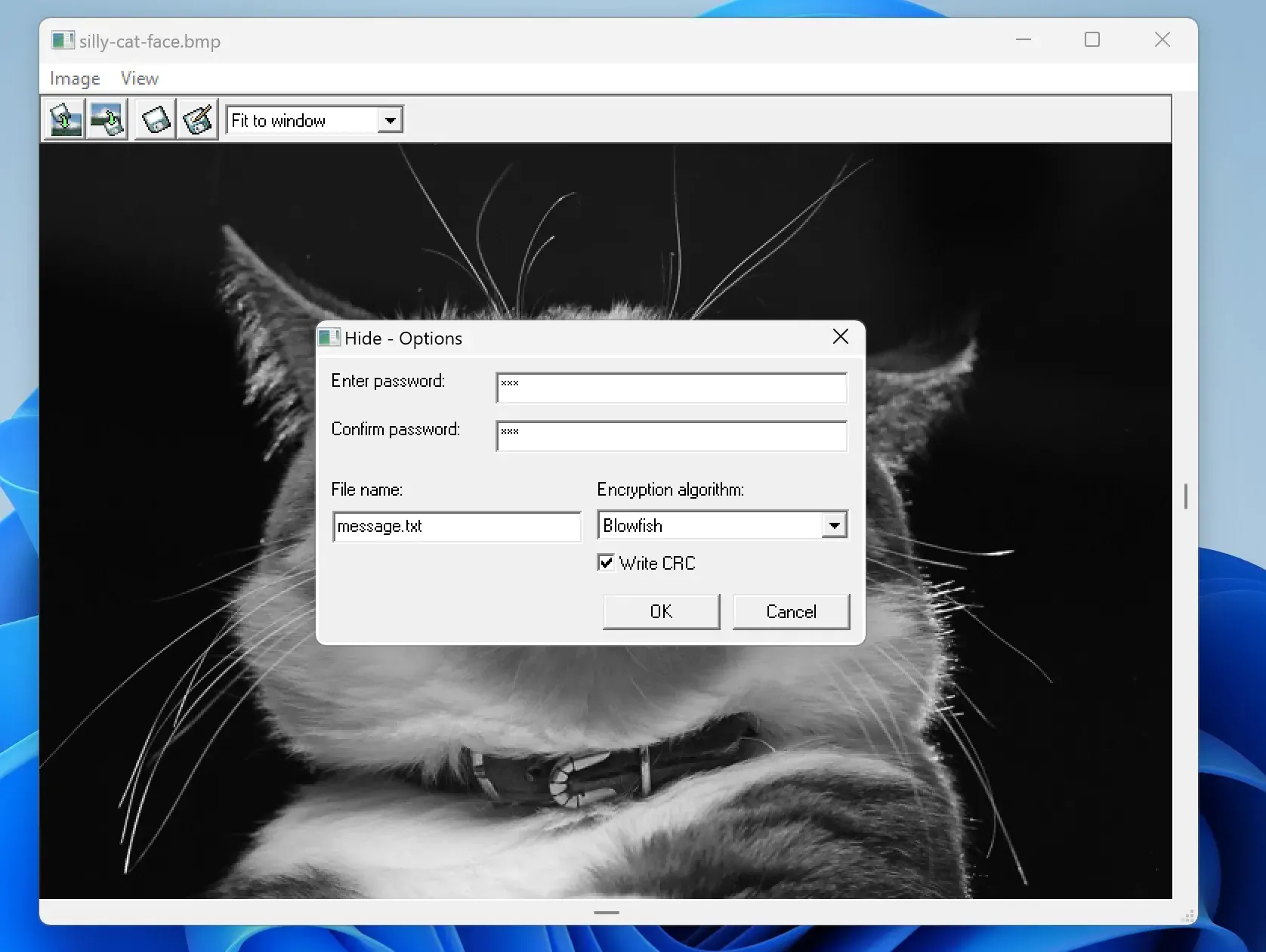
3. You will be introduced to entering a password to keep the secret file hidden:
4. From the Menu above Click on Image => Save Picture :
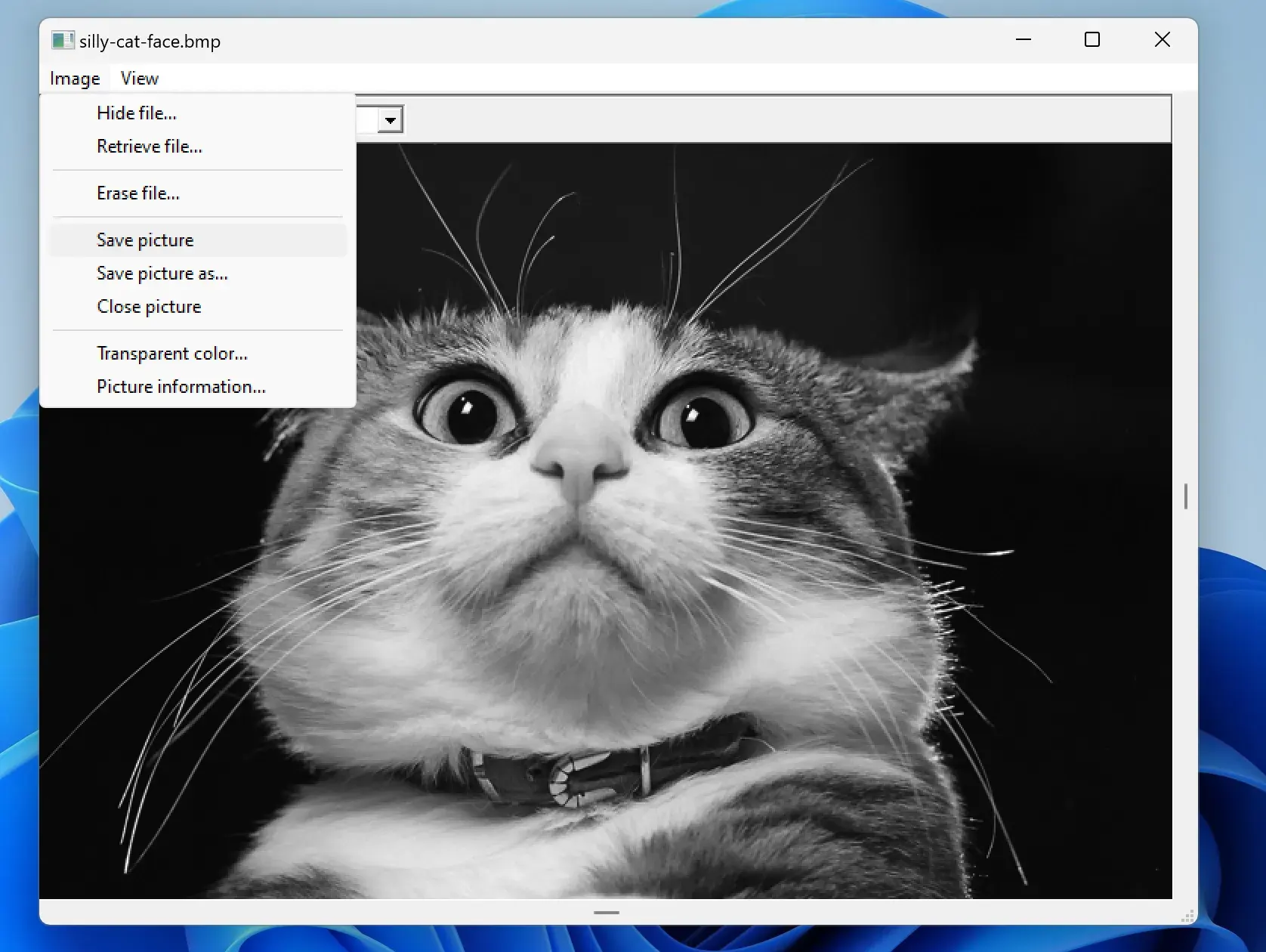
5. After the picture has been saved, you can open it in a new window, by clicking on Image => retrieve file From the Menu above:
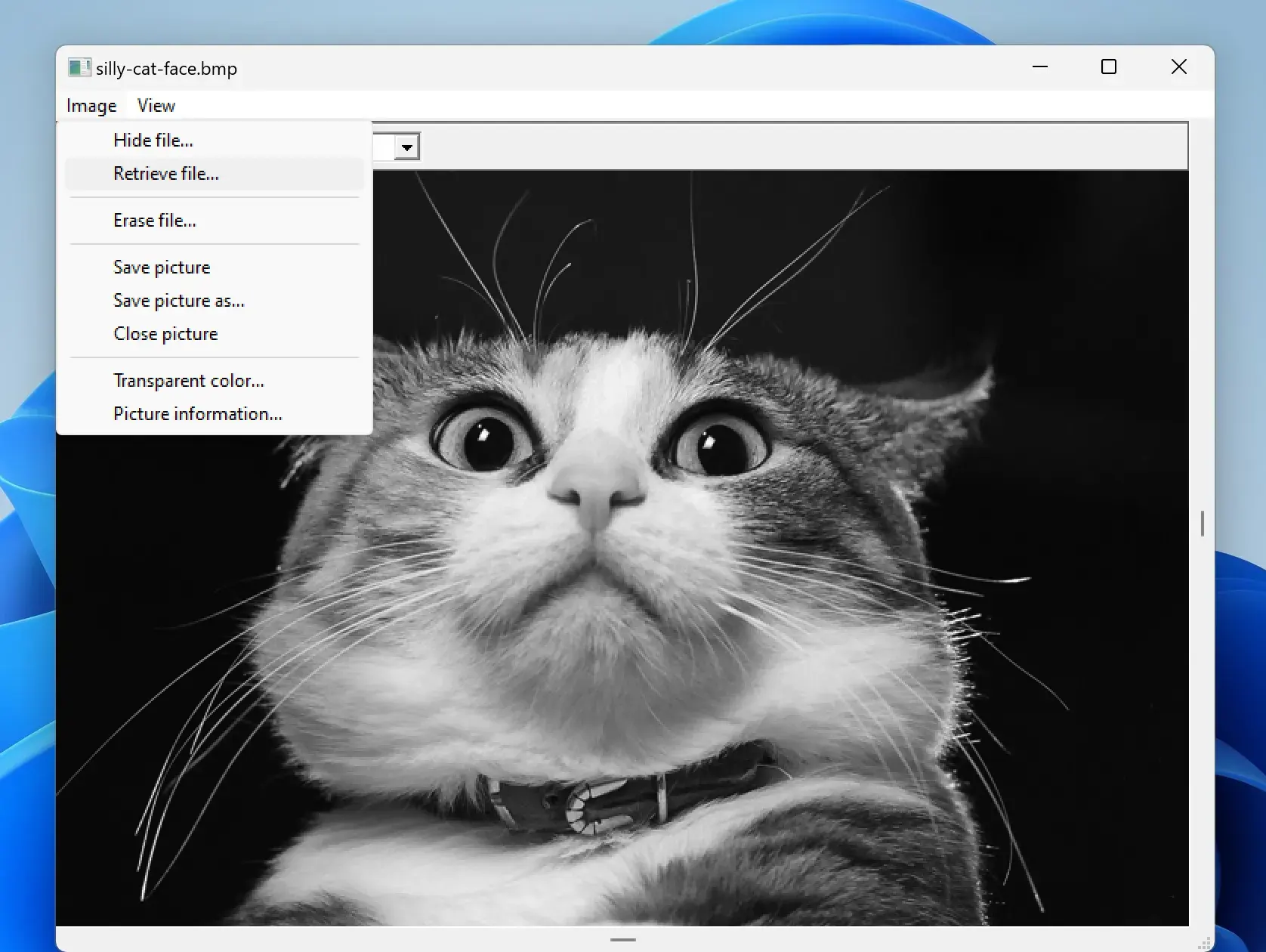
6. Insert the password that has been set to keep the secret text file safe:
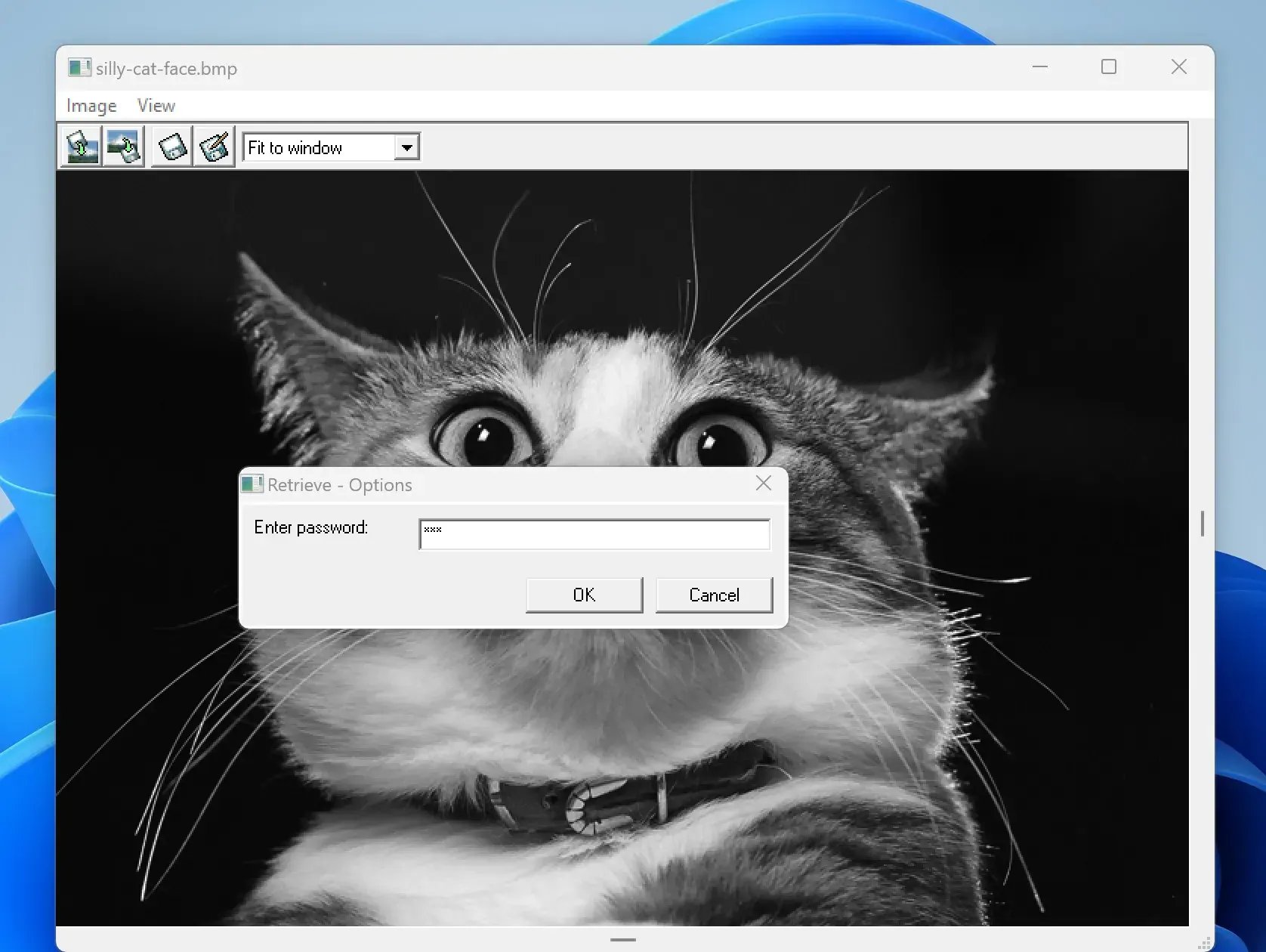
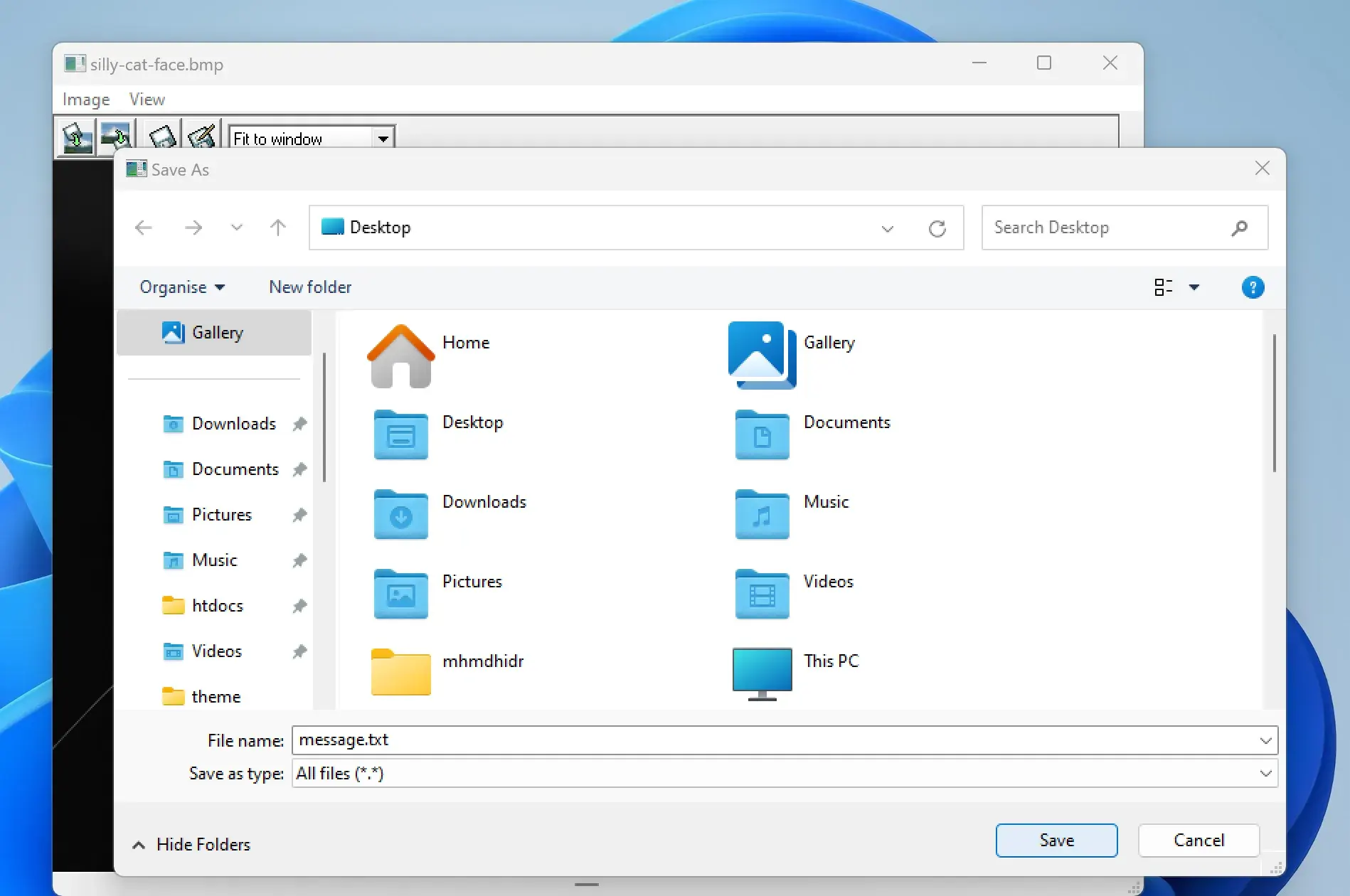
7. If the password is correct the file will be unlocked and you will be presented with the file save window to select a location for saving the file:
Results:-
I would characterize this as a Fragile steganography method because of its simplicity, minimal usage of inducing bugs or errors, and overall simplicity. In contrast, robust methods have the will lead to the loss of the hidden message if the image is compressed or altered in any way.
The link to the file with the hidden message: (Password to unlock is 123)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Js3N4-niinSs0Tku2VeE4JZWBq6ABx1y/view?usp=sharing
The Uncharted Territory
Despite its widespread use, steganography remains an enigmatic and evolving field. Its historical significance, modern-day applications, and implications continue to unfold in our interconnected digital world.
By delving into the realm of steganography, one can appreciate its historical significance and modern-day implications. It’s a topic that combines the art of secrecy with the science of data manipulation, making it both fascinating and highly relevant in today’s digital landscape.
References
-
University of Cambridge (n.d.) MP3 Steganography. [Online] Available at: http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~fapp2/steganography/mp3stego/ (Accessed: [Nov.2018]).
-
Darknet (2019) DeepSound - Audio Steganography Tool. [Online] Available at: https://www.darknet.org.uk/2019/03/deepsound-audio-steganography-tool/ (Accessed: [Mar.2019]).
-
Wikipedia (n.d.) Steganography. [Online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steganography (Accessed: [Oct.2023]).
-
[Ingemar J. Cox Matthew L. Miller Jeffrey A. Bloom Jessica Fridrich Ton Kalker] Digital Watermarking and Steganography. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780123725851/digital-watermarking-and-steganography (Accessed: [2008]).
-
What is Steganography? Types, Techniques, Examples & Applications [Online] Available at: https://www.simplilearn.com/what-is-steganography-article (Accessed: [Oct.20.2023]).